Thus, a higher ROCE indicates stronger profitability across company comparisons. I. The fixed assets are included in their net values, be it original cost or the replacement cost after depreciation. In times of inflation, super bowl 2021 commercials it is advisable to count fixed assets at the replacement cost which is actually the current market value of the assets. Capital employed can be analyzed to see how it affects a company’s overall performance.
Other Resources
The return on capital employed (ROCE) ratio is calculated by expressing profit before interest and tax as a percentage of total capital employed. ROE measures a company’s after-tax profits as a percentage of its shareholder equity. It shows how efficient the business is at generating profit with shareholder funds.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ROCE
Fundamental investors most frequently refer to capital employed as part of the return on capital employed (ROCE) or return on average capital employed (ROACE) metrics. ROCE and ROACE compare the company’s profitability to the total investments made in new capital. No fixed or universal definitions explain what capital employed means—or, rather, different definitions are based on different contexts. The simplest presentation of capital employed is total assets minus current liabilities.
What is ROCE?
Asset turnover This measures the ability of the organisation to generate sales from its capital employed. Generally, the higher the better, but in later studies you will consider the problems caused by overtrading (operating a business at a level not sustainable by its capital employed). Commonly a high asset turnover is accompanied with a low return on sales and vice versa. Retailers generally have high asset turnovers accompanied by low margins. A return on capital is necessary to reward investors for the risks they are taking by investing in the company. Generally, the higher the ROCE or ROE figure, the better it is for investors.
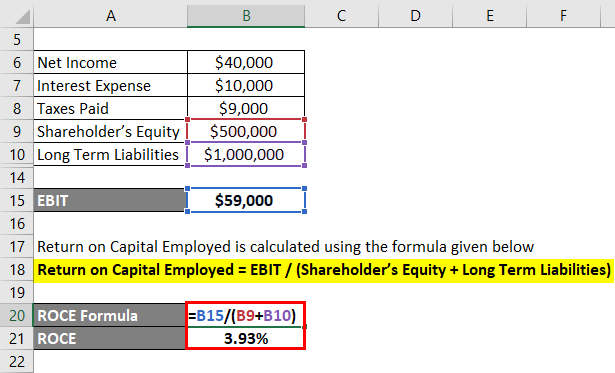
How Is Return on Capital Employed Calculated?
This determines how capital employed compares to capital going into a company. Working capital can be defined as a quick measure of the operational efficiency of a company and its overall financial health. A higher value of Capital Employed, especially when a significant chunk of it is not sourced from shareholders’ equity, indicates a higher risk level. Capital employed can impact a company’s valuation by influencing the return on investment and the risk profile of the business. Investors and potential buyers consider capital employed as an indicator of the resources available and the efficiency of capital utilization. A higher capital employed, if effectively managed, can positively influence a company’s valuation.

Example of How to Use ROCE
Although capital employed can be defined in different contexts, it generally refers to the capital utilized by the company to generate profits. The figure is commonly used in the Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) ratio to measure a company’s profitability and efficiency of capital use. The roce ratio determines the efficiency of a company in using its capital. A general approach to calculating capital employed from a given balance sheet is to deduct current liabilities from the total assets of the business. Generally, an acceptable ROCE exceeds a company’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC).
Its name is Synnex, a TI (technical information) company related to the data center business. Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice.
- Capital employed is capital that a business has used up on their capital fixed assets and capital working capital.
- Understanding this crucial financial metric is critical to assessing a company’s operational efficiency and overall financial health.
- These are earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) and capital employed.
- This could be developing new products or opening up stores in new locations.
- Capital employed, also called funds employed, refers to the total amount of invested capital a company uses for its operations and to generate profits.
While equity is usually more concerned with ownership and the financial returns to shareholders, capital employed gives better insight into the overall financial structure of a company. Capital employed is primarily used by analysts to determine the return on capital employed (ROCE). Like return on assets (ROA), investors use ROCE to get an approximation of what their return might be in the future. Quick ratio The quick ratio (acid test) recognises that inventory often takes a long time to convert into cash. In practice a company’s current ratio and quick ratio should be considered alongside the company’s operating cash flow.
That said, investors tend to prefer companies with stable and rising ROCE over a period of time, indicating a better business or improved management. In general, both the ROIC and ROCE should be higher than a company’s weighted average cost of capital (WACC) in order for the company to be profitable in the long term. Improving ROCE requires a strategic approach that focuses on enhancing profitability and capital efficiency.
It may also refer to how much capital has been used for a specific project. This could be developing new products or opening up stores in new locations. Any capital that is tied up in capital employed cannot be used for personal use. The average capital employed helps the analysts and investors decide the type of capital structure of the business, which is turn gives them an idea about how much is debt and how much is equity. This speaks about the repayment obligation which is a risk because money will flow out of the business.
ROCE is figured using earnings before interest and taxes divided by the company’s total capital, both equity and debt. While ROI can be used to compare products and investment opportunities, ROCE is more specific to companies. ROCE is calculated by dividing the company’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) by the capital employed. Capital employed can be calculated by adding shareholder’s equity and total debt, including both short-term and long-term debts. Some analysts prefer ROCE over ROA and ROE because the return on capital considers both debt and equity financing.
